|
|
Fern

|
Ferns are considered some of the oldest land plants on
earth, dating from 200 million years ago. Ferns are cryptogamous, or
spore-producing, plants. Found worldwide, ferns are capable of growing in
soil, water, on rocks, or on other plants. They range in size from a few
centimetres to nearly 24 m (80 ft) in height. The underground stems and the
fronds, or leaves, of some fern plants are edible.
Dorling
Kindersley
|
|
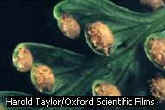
Underside
of a Fern Frond Showing Ripe Sori
|
An examination of the underside of a fern frond reveals
small, spore-bearing structures called sori. When the sori become mature,
they split open and release thousands of minute spores. Under favourable
conditions, the spores germinate and grow into small, heart-shaped plants
called prothalli. The prothalli produce ''eggs'' and ''sperm'', and,
following fertilization, a new fern plant called the sporophyte begins to
grow.
Harold Taylor/Oxford Scientific Films
|
|
Alternation
of Generations

|
Fernsí mode of reproduction includes what is called
alternation of generations. The mature fern plant, the sporophyte stage, is
the generation that produces spores. The spores are released into the air and
subsequently settle and germinate into a small, usually inconspicuous
generation called the gametophyte stage. This stage produces male and female
gametes, which fuse and grow into a new sporophyte stage.
Dr. C.E.
Jeffree/Oxford Scientific Films
|
|
Maidenhair Fern

|
The maidenhair fern, Adiantum capillus-veneris, a
deciduous fern found in termperate and subtropical areas worldwide, is
characterized by arching, light green fronds borne on black stems. It reaches
a height of 30 cm (12 in). The maidenhair fern grows best in shaded locations
with moist soils.
Dorling Kindersley
|
|
Soft Shield
Fern

|
The soft shield fern, Polystichum setiferum, is
cultivated for its attractive, soft-textured foliage. This species of fern
grows to a height of 60 cm (24 in). Ferns have become popular domestic
plants, displaying a wide variety of sizes, colours, and textures while being
relatively easy to grow.
Geoff Kidd/Oxford Scientific Films
|
|
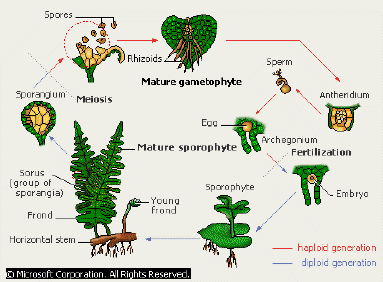
Life Cycle
of a Fern
|
On the underside of the leaves, groups of spore cases, or
sporangia, form. They are seen as small brown spots, known as sori. The spore
falls and begins to germinate, developing into a gametophyte called the
prothallus. On the underside of the prothallus are the female sexual organs
(archegonia) and the male sexual organs (antheridia). Fertilization of the
eggs in the archegonium takes place only in the presence of water. Only one
sporophyte plant develops from each prothallus. The parent prothallus then
dies.
© Microsoft Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
|
[Wild Life of the
Rainforest] [Documentary] [Home] |